
BIOCELL is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on molecular and cellular biosciences. The journal welcomes high quality original research articles, review papers, communications, perspectives, commentaries, etc. Topics of interests include but are not limited to: Cellular Biochemistry, Structural & Molecular Biology, Cellular/Molecular Biology, Immunology, Pathology & Neurobiology, Cell Signaling, Regenerative Biology & Stem Cells, Cancer Biology, RNA Biology, Genomics, Transcriptomics, Proteomics & Metabolomics, Plant Molecular & Cellular Biology.
Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE): 2022 Impact Factor 1.2; Journal Citation Report/Science Edition (JCR); Scopus; Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2022): 1.2; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2022): 0.379; Sociedad Argentina de Investigaciones en Bioquímica y Biología Molecular (SAIB); Portico, etc.
 Refers to the articles published on the journal within the last three years that have gained the most viewing times to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
Refers to the articles published on the journal within the last three years that have gained the most viewing times to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
 Refers to articles published on the journal since 2020 that have received the most frequent citation to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
Refers to articles published on the journal since 2020 that have received the most frequent citation to date (Statistics provided by TSP database)
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 677-692, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048873
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular Signal Transduction in Biological Activities)
Abstract The structural and associated molecules of the extracellular matrix (ECM) complex is an important component of the local milieu of cells, both for maintaining their functions and homeostasis. It is a dynamic structure that is finely tuned to changes in the microenvironment. One of these factors is hypoxia, which can arise in tissues due to physiological or pathological effects. As a result of the hypoxic effect, the properties of the ECM are significantly modified, stiffness increases, the balance between degradation and synthesis of structural proteins shifts, and the deposition of biologically active mediators’ changes. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) contribute significantly to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 693-706, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048776
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Exploring the Cellular Mechanisms of Neurodegenerative Diseases)
Abstract Physical activity and exercise have several beneficial roles in enhancing both physiological and psychological well-being of an individual. In addition to aiding the regulation of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, exercise can stimulate the synthesis of exerkine hormones in the circulatory system. Among several exerkines that have been investigated for their therapeutic potential, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is considered the most promising candidate, especially in the management of neurodegenerative diseases. Owing to the ability of physical activity to enhance BDNF synthesis, several experimental studies conducted so far have validated this hypothesis and produced satisfactory results at the pre-clinical level. This review… More >
Graphic Abstract
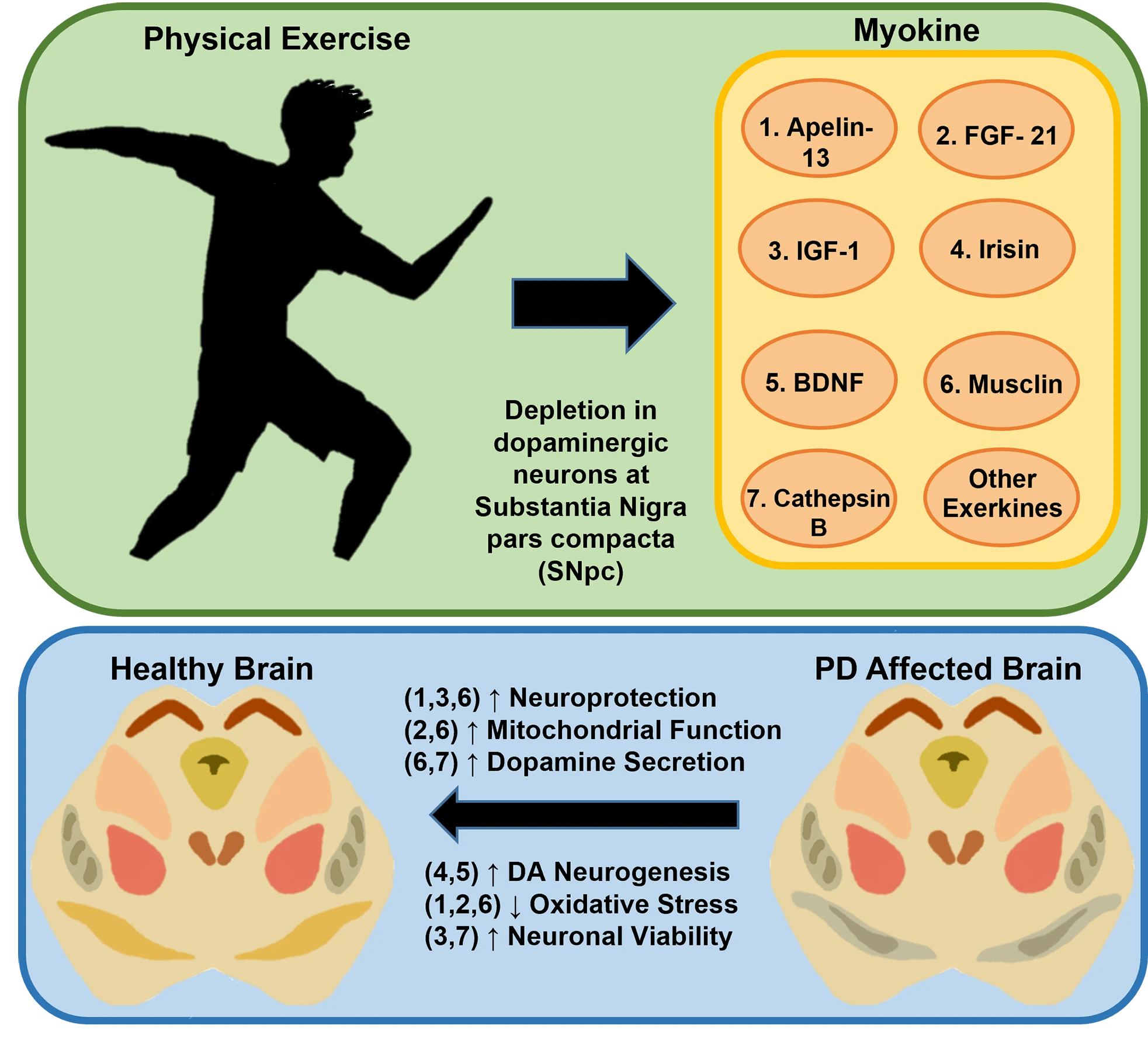
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 707-729, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.049130
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Exploring the Cellular Mechanisms of Neurodegenerative Diseases)
Abstract Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disease in the elderly, accounting for more than 1% of the population aged 65 years. Monogenic inheritance is relatively rare in PD, accounting for approximately 5% to 10% of PD patients, and there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that multiple genetic risk factors play a significant role in the pathogenesis of PD. Several groups have identified and reported a number of genes carrying mutations associated with affected family members. Mutated genes associated with PD are also candidates for idiopathic PD, and these genes may also carry other mutation sites that increase… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 731-744, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048820
Abstract Background: Depression is becoming increasingly prevalent around the world, imposing a substantial burden on individuals, families, as well as society. Quercetin is known to be highly effective in treating depression. However, additional research is needed to dissect the mechanisms of its anti-depressive effects. Methods: For this study, Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomized into the control, model, quercetin, or fluoxetine group. The latter three groups were exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) for 42 d. The first two groups received saline solution daily via oral gavage. Meanwhile, the quercetin group was orally administered a quercetin suspension (52.08 mg/kg) every day,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 745-758, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.049140
Abstract Background: Acute pancreatitis (AP), known for its rapid onset and significant incidence and mortality rates, presents a clinical challenge due to the limited availability of effective treatments and preventive measures. Anemarsaponin B (ASB) has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent, demonstrating capabilities in reducing immune inflammation, positioning it as a promising candidate for AP treatment. Methods: We investigated the effects of ASB on AP in mice, induced by caerulein and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Peripheral blood samples were collected 24 h post-induction with caerulein to assess of key biomarkers including lipase, amylase, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, SOD, and GSH-Px. A range of techniques… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 759-769, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048551
Abstract Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a global health concern with the acid sphingomyelinase (ASM)/ceramide (CE) pathway and the NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome identified as pivotal players in lipid disorders and inflammation. This study explores the interaction mechanism between the ASM/CE pathway and NLRP3 in NAFLD cell models, aiming to understand the impact of amitriptyline (Ami), an ASM inhibitor, on lipid deposition and hepatocyte injury by regulating the ASM/CE-NLRP3 pathway. Methods: HepG2 and HL-7702 cells were exposed to free fatty acids (FFAs) to establish the NAFLD model. The cells were divided into 5 groups:… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 771-792, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048878
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Biomarker Research: Unveiling the Pathways to Precision Medicine)
Abstract Background: Ferroptosis, a lipid peroxidation-mediated programmed cell death, is closely linked to tumor development, including prostate cancer (PCa). Despite established connections between ferroptosis and PCa, a comprehensive investigation is essential for understanding its impact on patient prognosis. Methods: A risk model incorporating four ferroptosis-related genes was developed and validated. Elevated risk scores correlated with an increased likelihood of biochemical recurrence (BCR), diminished immune infiltration, and adverse clinicopathological characteristics. To corroborate these results, we performed validation analyses utilizing datasets from both the Cancer Genome Atlas Cohort (TCGA) and the Gene Expression Synthesis Cohort (GEO). Moreover, we conducted further investigations into the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 793-801, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048395
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Subcellular Organelles and Cellular Molecules: Localization, Detection, Prediction, and Diseases)
Abstract Background: Galectin 2 (LGALS2) is a protein previously reported to serve as a mediator of disease progression in a range of cancers. The function of LGALS2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), however, has yet to be explored, prompting the present study to address this literature gap. Methods: Overall, 144 paired malignant tumor tissues and paracancerous OSCC patient samples were harvested and the LGALS2 expression levels were examined through qPCR and western immunoblotting. The LGALS2 coding sequence was introduced into the pcDNA3.0 vector, to enable the overexpression of this gene, while an LGALS2-specific shRNA and corresponding controls were also obtained.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 803-815, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.047122
Abstract Background: Although it has been established that the human Solute Carrier Family 22 (SLC22) functions as a cationic transporter, influencing cellular biological metabolism by modulating the uptake of various cations, its impact on cancer prognosis remains unclear. Methods: We conducted a comprehensive analysis utilizing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and other databases to assess the prognostic value and functional implications across various tumors. Silence of SLC22A1 RNA in glioma U251 cells was performed to access the impact of SLC22A1 on lower-grade glioma (LGG) progression. Results: Our findings demonstrated a significant correlation between SLC22A1 expression and the survival time… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 817-834, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048737
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Frontiers in cancer: tumor microenvironment)
Abstract Background: The incidence of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is globally high; however, despite the introduction of innovative drug therapies, there remains a lack of effective biomarkers for evaluating treatment response. Recently, Caspase recruiting domain-containing protein 11 (CARD11) has garnered attention due to its significant association with tumor development and the immune system. Methods: The expression of CARD11 mRNA and protein in ccRCC were analyzed by public database and immunohistochemistry. The focus of this study is on the epigenomic modifications of CARD11, its expression of ccRCC immunophenotype, and its correlation with response to immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Furthermore, to… More >
Graphic Abstract
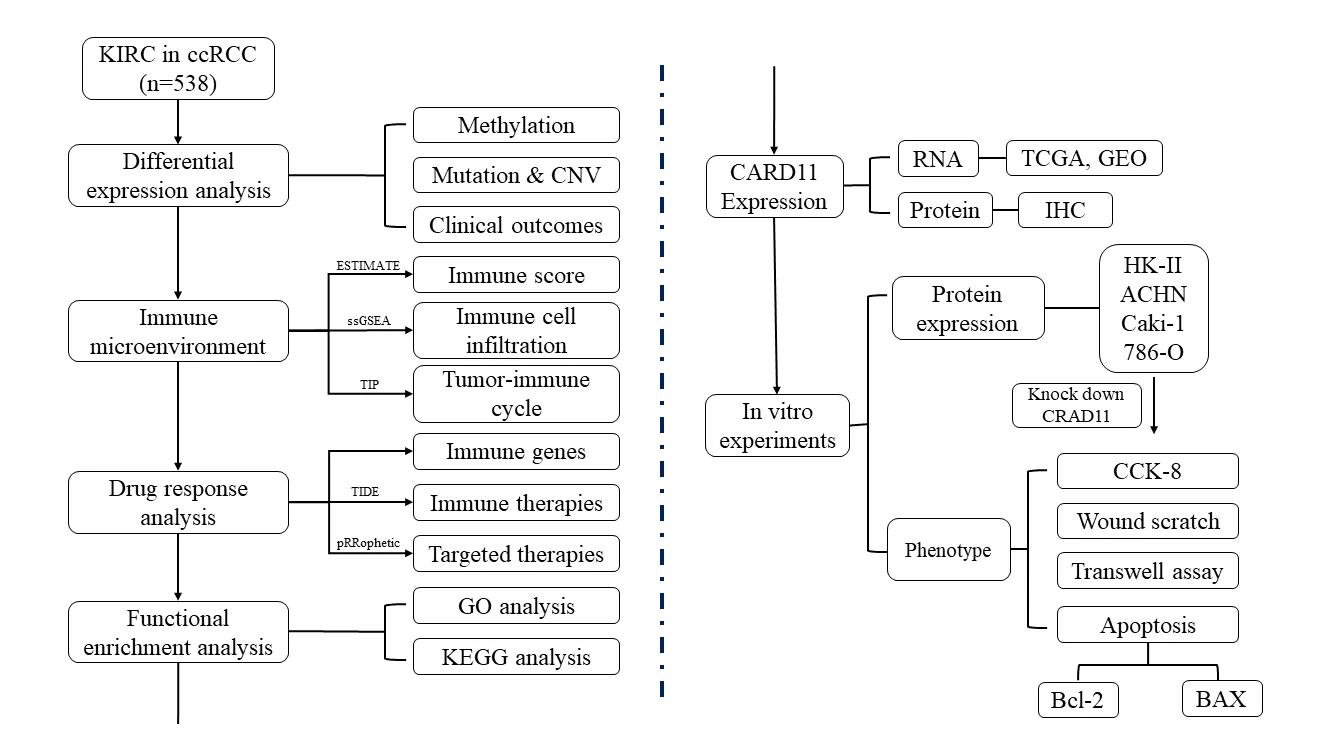
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 835-845, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048076
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Navigating the Interplay of Cancer, Autophagy, ER Stress, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Future Directions)
Abstract Background: The incidence of colorectal cancer (CRC) has been increasing in recent years. Thus, the discovery of factors that can assist in alleviating CRC is urgently warranted. Methods: To identify a potential factor involved in the development of CRC, we screened the upregulated genes in tumor tissues through four datasets from an online database. The expression of reticulocalbin 1 (RCN1), a Ca-binding protein, was upregulated in the four datasets. Based on loss-of-function experiments, the effect of RCN1 on cell viability was assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. The regulatory effect of RCN1 on apoptosis was evaluated through Annexin V-fluorescein… More >
Graphic Abstract
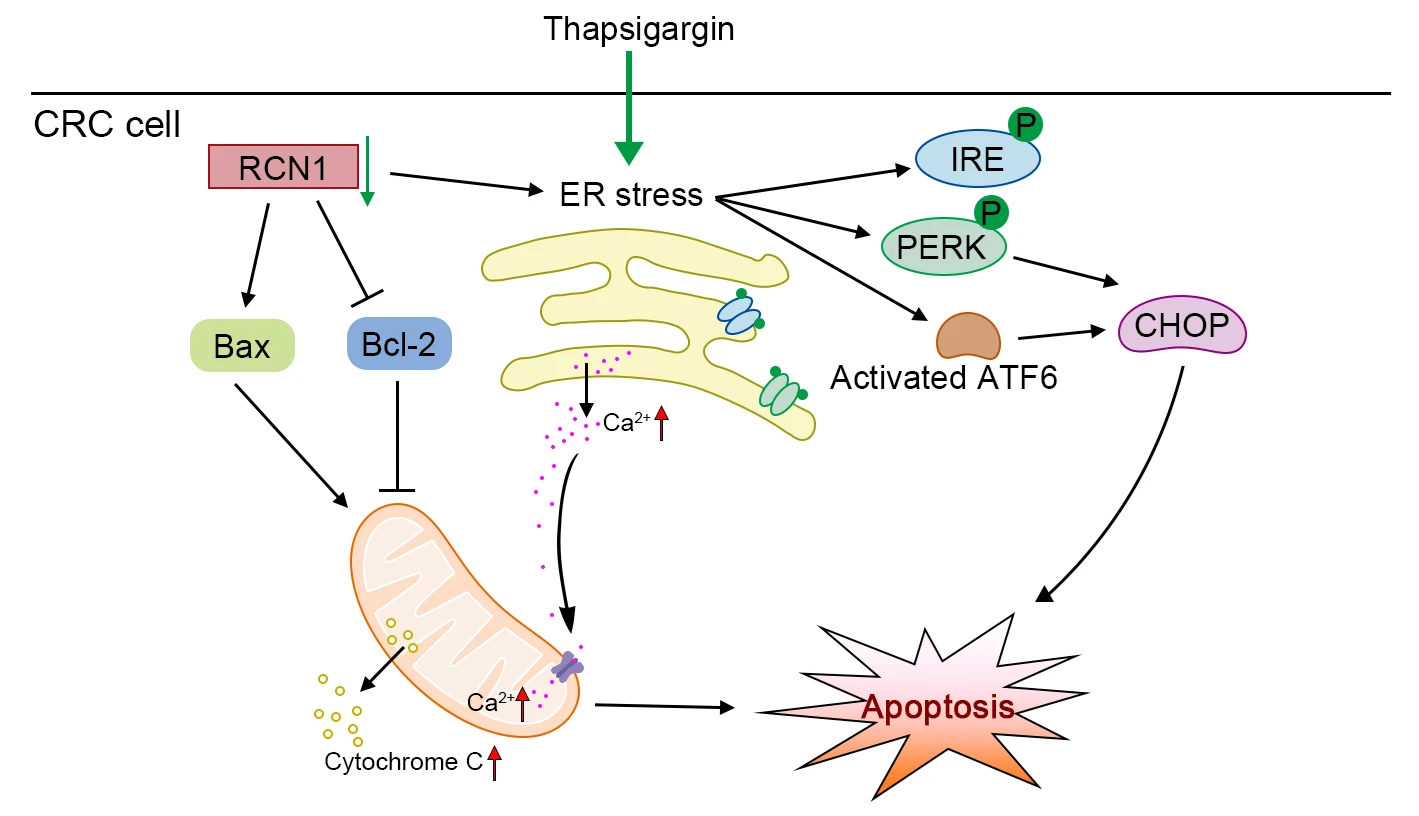
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 847-860, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.050868
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Navigating the Interplay of Cancer, Autophagy, ER Stress, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Future Directions)
Abstract Background: Regulatory proteins involved in human cellular division and proliferation, cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) are overexpressed in numerous cancers, including triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). TNBC is a common pathological subtype of breast cancer that is prone to recurrence and metastasis, and has a single treatment method. As one of the CDK4/6 inhibitors, abemaciclib can effectively inhibit the growth of breast tumors. In this study, we synthesized LA-D-B1, a derivative of Abemaciclib, and investigated its anti-tumor effects in breast cancer. Methods: Cellular viability was assessed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Cell cloning and migration abilities were determined by… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
BIOCELL, Vol.48, No.5, pp. 861-872, 2024, DOI:10.32604/biocell.2024.048758
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Navigating the Interplay of Cancer, Autophagy, ER Stress, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Future Directions)
Abstract Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) exhibits a significant prevalence in the southern regions of China, and paclitaxel (PTX) is frequently employed as a medication for managing advanced NPC. However, drug resistance is typically accompanied by a poor prognosis. Exploring the synergistic potential of combining multiple chemotherapeutic agents may represent a promising avenue for optimizing treatment efficacy. Methods: This study investigated whether 3-Methyladenine (3-MA) could potentiated the effect of PTX and its potential molecular mechanism. Samples were divided into the following categories: Negative control (NC) with the solvent dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 0.5% v/v), PTX (400 nM), 3-MA (4 mM), and PTX (400… More >